The global Event Stream Processing Industry size is projected to grow from USD 930.4 Million in 2023 to USD 2400.1 Million by 2030, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.86% during the forecast period. The report cites factors such as the increasing demand for real-time streaming analytics, the growing adoption of IoT devices, and the rise of big data analytics as drivers of this growth.
In today's data-driven world, businesses need to extract real-time insights from vast amounts of streaming data to stay competitive. Event Stream Processing (ESP) has emerged as a powerful technology that enables organizations to analyze and act upon streaming data in real time. This article explores the concept of event stream processing, its benefits, key components, and its potential impact on businesses.
- Understanding Event Stream Processing
Event Stream Processing is a technology that allows organizations to process, analyze, and derive meaningful insights from continuous streams of data in real time. It involves capturing, filtering, aggregating, and transforming data as it flows through a stream processing engine, enabling immediate actions and decision-making based on up-to-date information.
- Key Components of Event Stream Processing
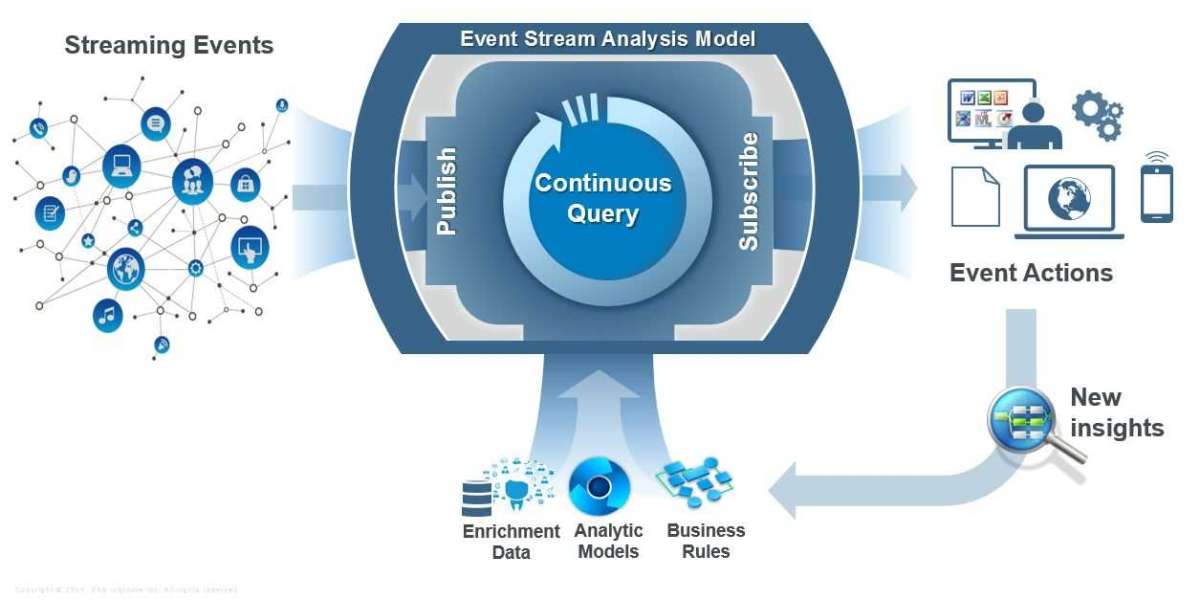
Event Stream Processing comprises several key components:
Get Sample PDF Pages now with Some Benefits!! https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/sample_request/7491
a. Stream Sources: Stream sources are the origins of streaming data, such as sensors, IoT devices, social media feeds, transaction logs, and more. These sources generate a continuous flow of data that is processed in real time.
b. Stream Processing Engine: The stream processing engine is the core component responsible for ingesting, processing, and analyzing streaming data. It applies various operations, such as filtering, aggregating, joining, and enriching data, to extract valuable insights.
c. Event Time Processing: Event time processing is a key aspect of event stream processing that considers the timestamps associated with each event. It enables accurate analysis of data based on the event's occurrence time, even when events arrive out of order.
d. Event Stream Analytics: Event stream analytics involves applying advanced analytics techniques, such as pattern recognition, anomaly detection, machine learning, and complex event processing, to gain valuable insights from streaming data in real time.
- Benefits of Event Stream Processing
Event Stream Processing offers numerous benefits to organizations:
a. Real-Time Insights: ESP enables organizations to analyze and act upon streaming data in real time. This provides timely insights, enabling immediate actions, proactive decision-making, and faster response to critical events and opportunities.
b. Continuous Monitoring and Alerting: With ESP, organizations can monitor streaming data continuously for specific patterns, conditions, or anomalies. This allows for real-time alerting and triggering automated responses to address potential issues or seize business opportunities.
c. Operational Efficiency: ESP optimizes operational efficiency by processing data in real time, reducing latency, and enabling timely actions. It enhances process automation, improves resource allocation, and streamlines operational workflows.
d. Enhanced Customer Experience: Real-time analysis of streaming data allows organizations to deliver personalized and contextual experiences to customers. By leveraging ESP, businesses can respond promptly to customer needs, provide targeted offers, and optimize customer interactions.
- Impact on Businesses
Implementing event stream processing has a transformative impact on businesses:
a. Real-Time Decision-Making: ESP empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on the most current and relevant data. It enables proactive responses to changing market conditions, customer demands, and operational events.
b. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: By analyzing streaming data in real time, ESP enables predictive and prescriptive analytics. It helps identify emerging trends, predict future events, and recommend optimal actions to drive business success.
c. Fraud Detection and Security: ESP plays a crucial role in fraud detection and security by analyzing streaming data for suspicious patterns or anomalies. It enables real-time alerts, fraud prevention, and immediate response to security threats.
d. IoT and Edge Computing: Event stream processing is instrumental in harnessing the power of IoT and edge computing. It enables real-time analysis of sensor data, IoT device data, and edge-generated data, unlocking valuable insights and enabling automated actions.
Conclusion
Event Stream Processing is revolutionizing how businesses analyze and act upon streaming data in real time. With its ability to provide real-time insights, continuous monitoring, operational efficiency, and enhanced customer experiences, ESP empowers organizations to stay competitive in a fast-paced and data-driven world. By leveraging event stream processing, businesses can drive real-time decision-making, predictive analytics, fraud detection, and embrace the potential of IoT and edge computing. As organizations adopt event stream processing, they unlock new opportunities for innovation, agility, and success in today's digital landscape.