Intrusion Detection System Market
Intrusion Detection System Market share is expected to reach USD 8.18 Billion by 2030, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.11% during the forecast period. In today's interconnected digital landscape, the security of computer networks and systems has become paramount. Organizations and individuals are constantly under threat from cybercriminals who seek to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or other malicious purposes. To mitigate these risks, the use of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) has emerged as a critical component of cybersecurity strategies.
Introduction to Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
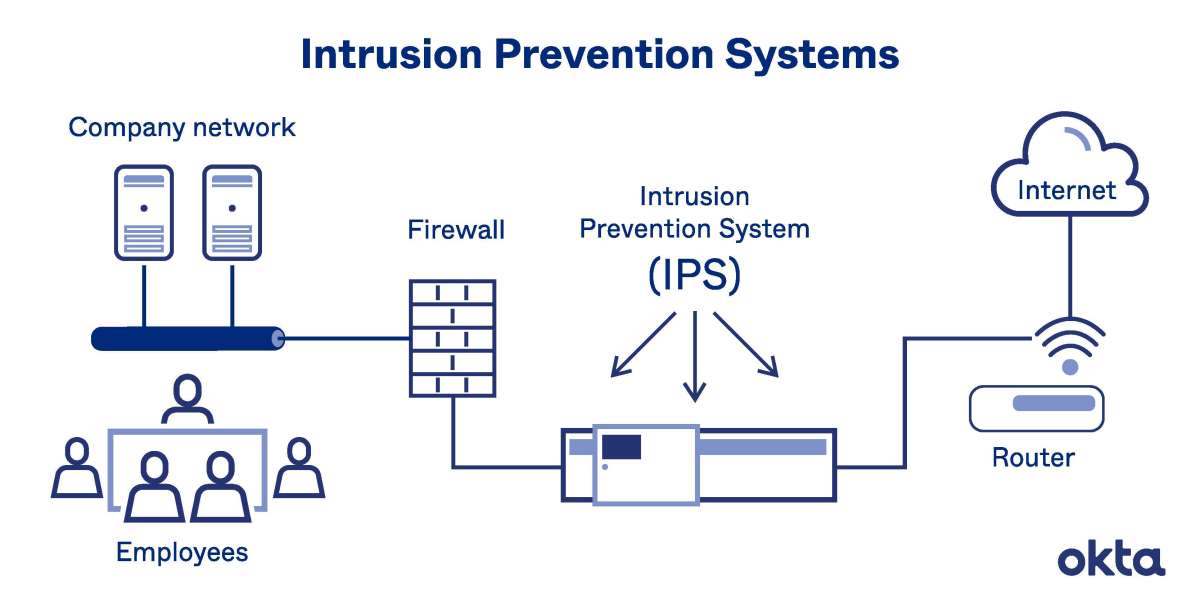
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security technology designed to monitor network traffic and system activities to identify and respond to unauthorized access or malicious activities. It acts as a vigilant guardian, constantly analyzing network traffic patterns and behaviors to detect potential threats in real-time.
Importance of IDS in Cybersecurity
With the increasing sophistication of cyber attacks, traditional security measures such as firewalls and antivirus software are no longer sufficient. IDS plays a crucial role in enhancing network security by providing an additional layer of defense. It helps in the early detection of intrusion attempts, enabling prompt response and mitigation actions.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
There are several types of IDS, each with its own approach to detecting and responding to intrusions. The three main categories are:
- Host-based IDS
Host-based IDS monitors activities on individual computers or servers. It analyzes system logs, file integrity, and user behavior to identify any suspicious or malicious activities occurring at the host level.
- Network-based IDS
Network-based IDS examines network traffic, analyzing packet headers and payloads to detect anomalies or known attack signatures. It operates at the network level and can monitor multiple devices within a network.
- Hybrid IDS
Hybrid IDS combines the capabilities of both host-based and network-based IDS. It provides comprehensive coverage by monitoring activities at both the host and network levels, offering a more holistic approach to intrusion detection.
Working Principles of IDS
IDS employs various detection techniques to identify potential threats. The three primary detection methods are:
- Signature-based Detection
Signature-based detection compares incoming network traffic or system activities against a database of known attack signatures. If a match is found, it indicates a potential intrusion attempt.
- Anomaly-based Detection
Anomaly-based detection focuses on identifying deviations from normal patterns of network or system behavior. It establishes a baseline of expected behavior and raises alerts when activities fall outside the established norms.
- Behavior-based Detection
Behavior-based detection observes and profiles the behavior of users or network entities to identify suspicious or abnormal actions. It looks for deviations from typical behavior patterns, which could indicate unauthorized access or malicious intent.
Advantages of Using an IDS
Implementing an IDS brings several benefits to organizations:
- Early Threat Detection
IDS provides early warning signs of potential security breaches, allowing organizations to respond quickly and mitigate risks before significant damage occurs.
- Reduced Response Time
By automatically alerting security teams to potential threats, IDS reduces the time it takes to identify and address security incidents. This rapid response minimizes the impact of cyber attacks.
- Protection against Zero-Day Attacks
IDS can detect zero-day attacks, which are previously unknown vulnerabilities exploited by hackers. With its anomaly-based and behavior-based detection capabilities, IDS can identify suspicious activities even when no specific signature exists.
Challenges and Limitations of IDS
While IDS offers significant advantages, it also faces some challenges and limitations:
- False Positives and Negatives
IDS systems may generate false positive alerts, flagging benign activities as potential threats. Conversely, false negatives can occur when IDS fails to detect actual attacks. Striking the right balance between accurate detection and minimizing false alarms is a constant challenge.
- Evading Detection Techniques
Sophisticated attackers can employ evasion techniques to bypass IDS detection mechanisms. By using encryption, obfuscation, or other techniques, they can evade signature-based detection and mimic normal behavior, making their activities harder to detect.
- Scalability and Performance Issues
For large-scale networks, the deployment and management of IDS can be complex. IDS systems need to handle substantial amounts of network traffic without impacting network performance. Ensuring scalability and efficiency are important considerations.
Market Overview of IDS
The intrusion detection system market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing need for robust cybersecurity solutions. The market has seen a surge in adoption across various industries, including finance, healthcare, government, and IT.
Growth and Adoption Trends
The IDS market is experiencing steady growth due to the rising number of cyber threats and the growing awareness of the importance of proactive security measures. Organizations are increasingly investing in IDS solutions to protect their sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
The IDS market can be segmented based on deployment mode, organization size, and end-user industry. The deployment modes include on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid models. Organization size segments encompass small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises. Various industries, such as banking and finance, healthcare, government, and IT, are prominent adopters of IDS solutions.
Key Players in the IDS Market
The IDS market features a competitive landscape with several key players offering innovative solutions. Some of the leading companies in the market include Cisco Systems, IBM Corporation, Trend Micro Incorporated, Palo Alto Networks, and Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
Factors Driving the IDS Market
Several factors are propelling the growth of the IDS market:
- Increasing Cyber Threats and Data Breaches
The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats poses significant risks to organizations. High-profile data breaches and the financial implications associated with them have highlighted the need for robust IDS solutions.
- Stringent Government Regulations
Governments worldwide are enacting stringent cybersecurity regulations, compelling organizations to implement advanced security measures. Compliance requirements drive the adoption of IDS solutions to ensure adherence to industry-specific standards and safeguard critical data.
- Growing Adoption of Cloud Computing
The rapid adoption of cloud computing has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. IDS solutions are crucial in securing cloud environments and detecting potential intrusions or unauthorized access to cloud-based systems.
- Industry Applications of IDS
The application of IDS spans across various industries:
- Financial Institutions
Banks and financial institutions handle vast amounts of sensitive customer data and face constant threats of cyber attacks. IDS helps them monitor network traffic, identify potential threats, and protect against unauthorized access to financial systems.
- Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare sector, IDS plays a vital role in safeguarding patient information, medical records, and critical healthcare infrastructure. It helps identify and prevent data breaches, ensuring compliance with stringent healthcare regulations.
- Government and Defense
Government agencies and defense organizations handle classified information and face persistent cyber threats. IDS enables them to detect and respond to advanced persistent threats, ensuring the security of sensitive government systems and critical infrastructure.
- IT and Telecom
The IT and telecom industry relies heavily on network infrastructure, making them prime targets for cyber attacks. IDS solutions help detect and mitigate threats, protecting vital communication networks and sensitive customer data.
Future Trends and Innovations in IDS
The future of IDS is poised for significant advancements and innovations:
- Machine Learning and AI Integration
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing the field of cybersecurity. IDS systems are incorporating these technologies to enhance threat detection capabilities, enabling more accurate and adaptive responses to emerging threats.
- Cloud-based IDS Solutions
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, the demand for cloud-based IDS solutions is on the rise. Cloud-based IDS offers scalability, flexibility, and centralized management, making it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes.
- IoT and Industrial Control Systems Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and industrial control systems (ICS) presents new security challenges. IDS is evolving to address these challenges, providing specialized detection and protection mechanisms for IoT and ICS environments.
Conclusion
Intrusion Detection Systems are essential tools in the fight against cyber threats. They provide proactive detection and response capabilities, helping organizations safeguard their networks, systems, and critical data. With the increasing sophistication of cyber attacks, the IDS market is expected to witness continued growth and innovation.